| Post applies to: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azure SQL VM |
Running SQL Server on virtual servers in Azure (referred to as Infrastructure as a Service or IaaS for short) brings lots of great advantages and cost savings over managing your own physical hosts but not as many advantages as running databases in a fully managed service environment such as Azure SQL Database (referred to as Platform as a Service or PaaS for short).
A fully managed PaaS offering like Azure SQL DB automates a lot of the mundane but critical database administrative tasks such as auto-patching, Point In Time backups, database tuning and auditing amongst others.
Fortunately you can now take advantage of some of the managed service capabilities for you SQL Server VMs by PaaS-ifying them using the new SQL VM Resource Provider.
- Once the SQL VM Resource Provider is configured, SQL IaaS VMs display an additional SQL Virtual Machine in the Azure Portal
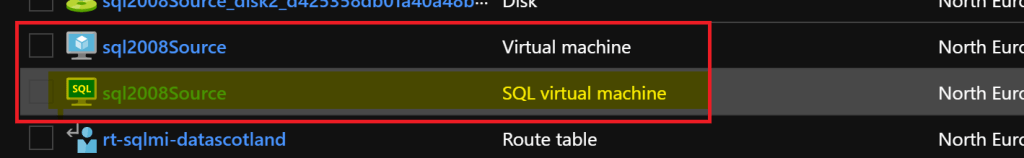
- This allows the configuration of PaaS type capabilities for IaaS eg auto-patching, back-ups etc
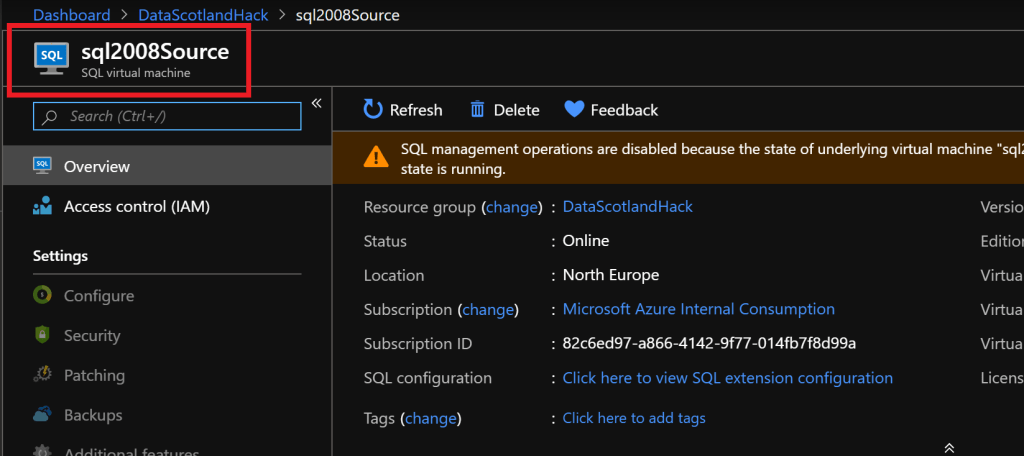
- For SQL Resource Provider to be enabled the IaaS VM must be registered for SQL RP so the Azure PaaS services know to take back-up, apply patches etc
Registering a SQL VM with the SQL Resource Provider
- In order for SQL Resource Provider to be enabled the SQL instance must be “registered”
- Marketplace SQL images are auto registered
- Build-your-own SQL VMs aren’t
- Registering of self-built SQL VMs is done via PowerShell/Azure CLI script details of which can be found here:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/sql/virtual-machines-windows-sql-register-with-resource-provider?tabs=powershell
For more details on how to register your SQL Server VMs check out the official documentation here: